Research
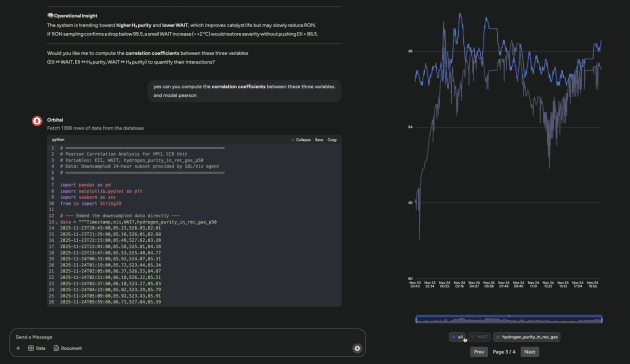
Orbital is an agentic, physics-informed AI multi-agent system that fuses first-principles physics models, time-series deep learning model, and LLM-based reasoning to deliver interpretable prediction, root-cause analysis and optimisation recommendation for heavy industry operations.
April 2025
A self-supervised monocular video depth framework that enforces temporal and geometric consistency without offline SfM, using diffusion-based temporal refinement and implicit scene-flow modelling to enable stable, online depth estimation in dynamic scenes
Dec 2024
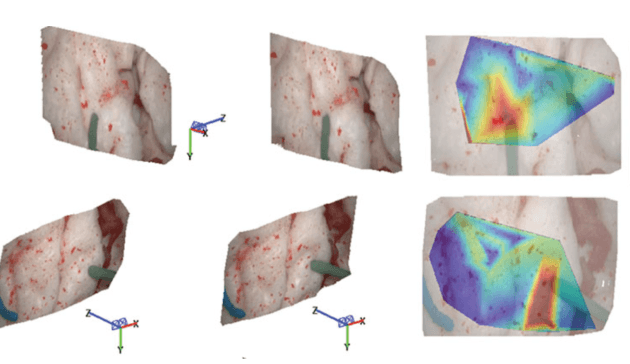
Generalizable and accurate stereo depth estimation is vital for 3D reconstruction, especially in surgery. Supervised learning methods obtain best performance however, limited ground truth data for surgical scenes limits generalizability.
Dec 2023
We present an extension to masked autoencoders (MAE) which improves on the representations learnt by the model by explicitly encouraging the learning of higher scene-level features. We do this by: (i) the introduction of a perceptual similarity term between generated and real images (ii) incorporating several techniques from the adversarial trainin...
Dec 2022
Introduces SurgT, the first standardised benchmark for soft-tissue tracking in stereo endoscopic surgery, providing a large-scale dataset, novel evaluation metrics, and a public challenge to advance unsupervised deep learning methods for surgical tracking
Aug 2023
My PhD thesis introducing self-supervised generative models, diffusion-based video depth, and implicit scene-flow learning to achieve sub-millimetre, temporally consistent depth estimation for mixed-reality surgical guidance
May 2023
Accurate stereo depth estimation is crucial for 3D reconstruction in surgery. Self-supervised approaches are more preferable than supervised approaches when limited data is available for training but they can not learn clear discrete data representations. In this work, we propose a two-phase training procedure which entails: (1) Performing Contrast...
Sep 2022
A self-supervised end-to-end deep learning framework that reconstructs occluded scenes in minimally invasive surgery and normal day-to-day videos, using generative spatio-temporal convolution to provide intraoperative see-through vision
July 2022
An evolutionary neural architecture that automatically designs and optimises deep multimodal networks, learning joint representations of ICU time-series, clinical events, and medical text to predict deterioration trajectories
May 2022
A survey of meta-learning methods that enable models to learn new tasks from limited data, with a focus on data-efficient learning and applications in medical AI
Mar 2022
A comprehensive survey of AI-enabled surgical robotics, covering perception, intraoperative decision-making, and the progression from human-in-the-loop assistance to context-aware autonomous surgery
Feb 2022
A plethora of deep learning-based methods have been proposed for self-supervised monocular depth estimation. The majority of these models utilise a U-Net-based architecture for disparity estimation. However, this architecture may not be optimal, and as shown in self-supervised approaches, replacing standard U-Net encoder with more complex architect...
Feb 2022
Surgical robots rely on robust and efficient computer vision algorithms to be able to intervene in real-time. The main problem, however, is that the training or testing of such algorithms, especially when using deep learning techniques, requires large endoscopic datasets which are challenging to obtain, since they require expensive hardware, ethica...
Feb 2021
Deep reinforcement learning has the potential to train robots to perform complex tasks in the real world without requiring accurate models of the robot or its environment. A practical approach is to train agents in simulation, and then transfer them to the real world. One of the most popular methods for achieving this is to use domain randomisation...
Dec 2019